Examples: Nonplanar Wakes
The induced drag of a nonplanar system can be lower than that of a planar system of the same lift and span. This is true even when the wing surfaces themselves are co-planar, but their vortex wakes are not. Examples of this phenomena include:
- America's Cup sailboat keels. Here the keel and rudder (or twin keel surfaces) are coplanar, but due to the substantial leeway angle and longitudinal displacement of the two surfaces, the wake downstream of the boat resembles that of a biplane system and the induced drag is reduced substantially.
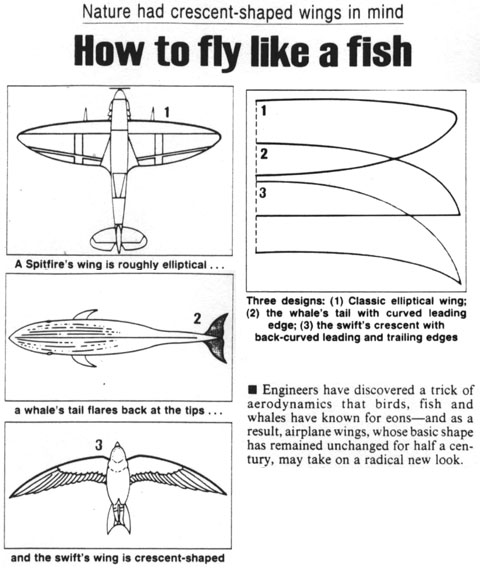
- Crescent wings. This phenomenon was postulated as the reason for the distinctive planform shape of some bird wings and fish fins, although the effect is almost unmeasurable.
- Split-Tips. This design was created to exploit the nonplanar wake geometry and is discussed in more detail in a subsequent section of this paper.
Ilan Kroo (kroo@leland.stanford.edu)

